
IgG Autoantibody Profile Examined in Established Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Rheumatology Advisor
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic, occasionally life-threatening, multisystem immune-mediated disorder. Patients may present with a wide array of symptoms, signs, and laboratory findings and have a variable prognosis that depends upon the disease severity and type of organ involvement. Establishing the diagnosis of SLE may be.

Lupus Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Causes, Sign & Symptoms
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a generalized disorder that can affect any system. Symptoms and signs may accumulate over time. The diagnosis is made using 2019 criteria recommended by the American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatology.

Managing Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Updated 2019 EULAR Released Medical Bag
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic multisystem autoimmune disease that is highly heterogeneous in its presentation. This can pose significant challenges for physicians responsible for the diagnosis and treatment of such patients. SLE arises from a combination of genetic, epigenetic and environmental factors.

Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and the Neutrophil NEJM
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a multisystem autoimmune disease that predominantly affects women of childbearing age and is the most common form of lupus. The exact cause is still unknown, but hormonal and immunological features and genetic predisposition are considered likely etiological factors.

Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) MedicoInfo
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a multisystem autoimmune disease with protean manifestation. Although commonly seen in young women, it can affect men as well as elderly patients. Approach to treatment is multidisciplinary, involves defining the extent of organ involvement, and distinguishing between active manifestations and damage. The mainstay of therapy is judicious use of immunosuppressive.

What Is Systemic Lupus Erythematosus;Diagnosis And Treatment
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a chronic autoimmune inflammatory connective tissue disorder that can involve joints, kidneys, skin, mucous membranes, and blood vessel walls. Problems in the joints, nervous system, blood, skin, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, lungs, and other tissues and organs can develop.

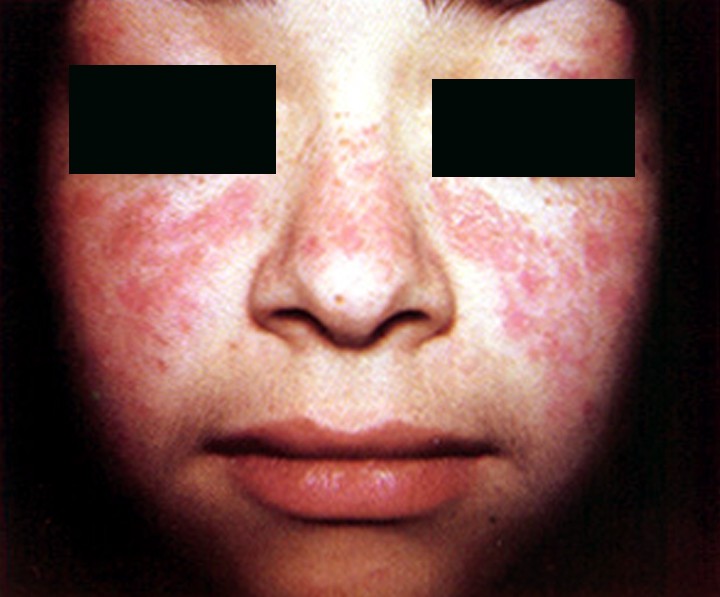
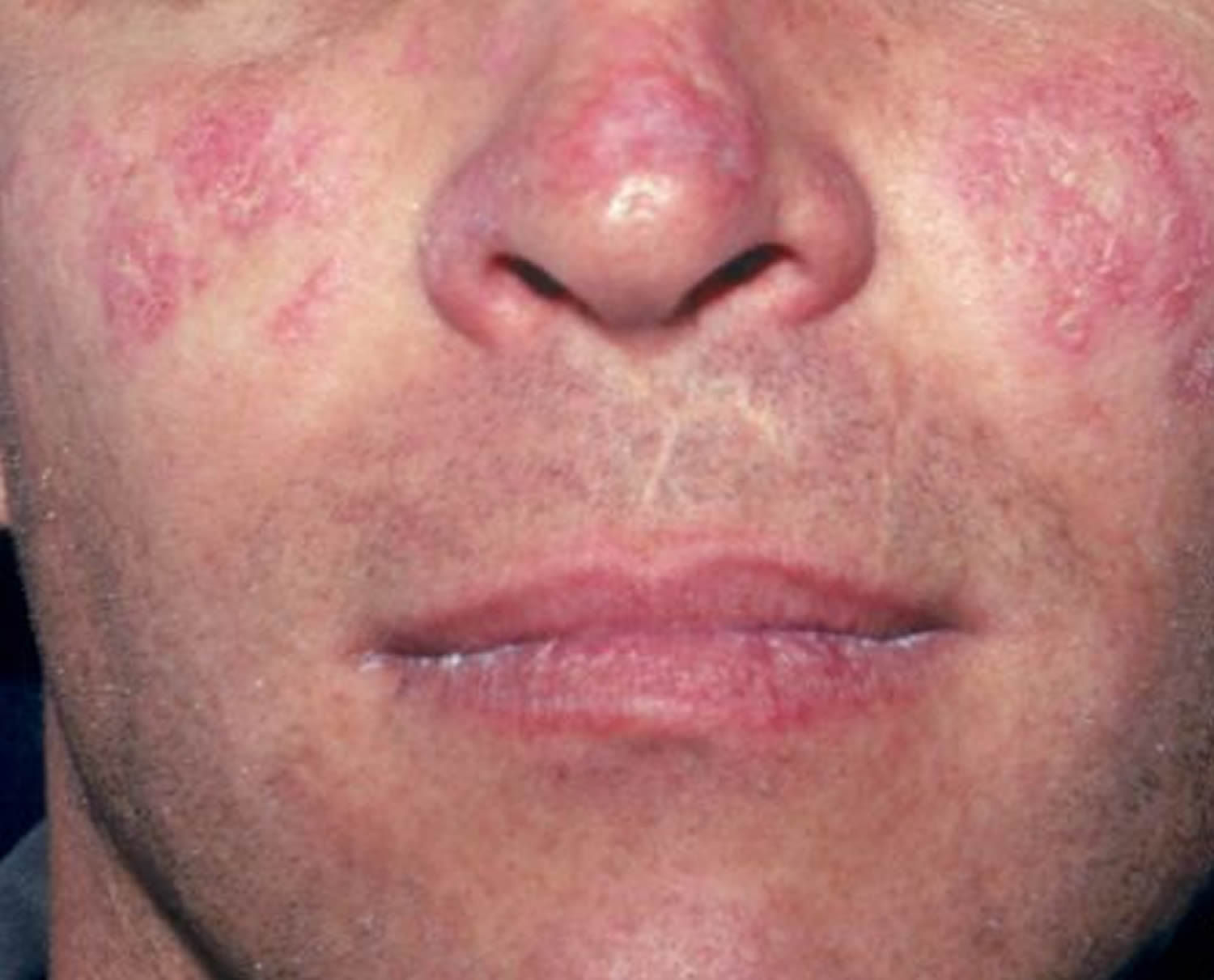
Facial Rash Of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (sle) Poster by Dr H.c.robinson/science Photo
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a heterogeneous autoimmune disease with a varying clinical course and prognosis. Signs and symptoms of SLE can be subtle or robust, affect a single organ system or several, and change over time, making it a difficult disease to diagnose.
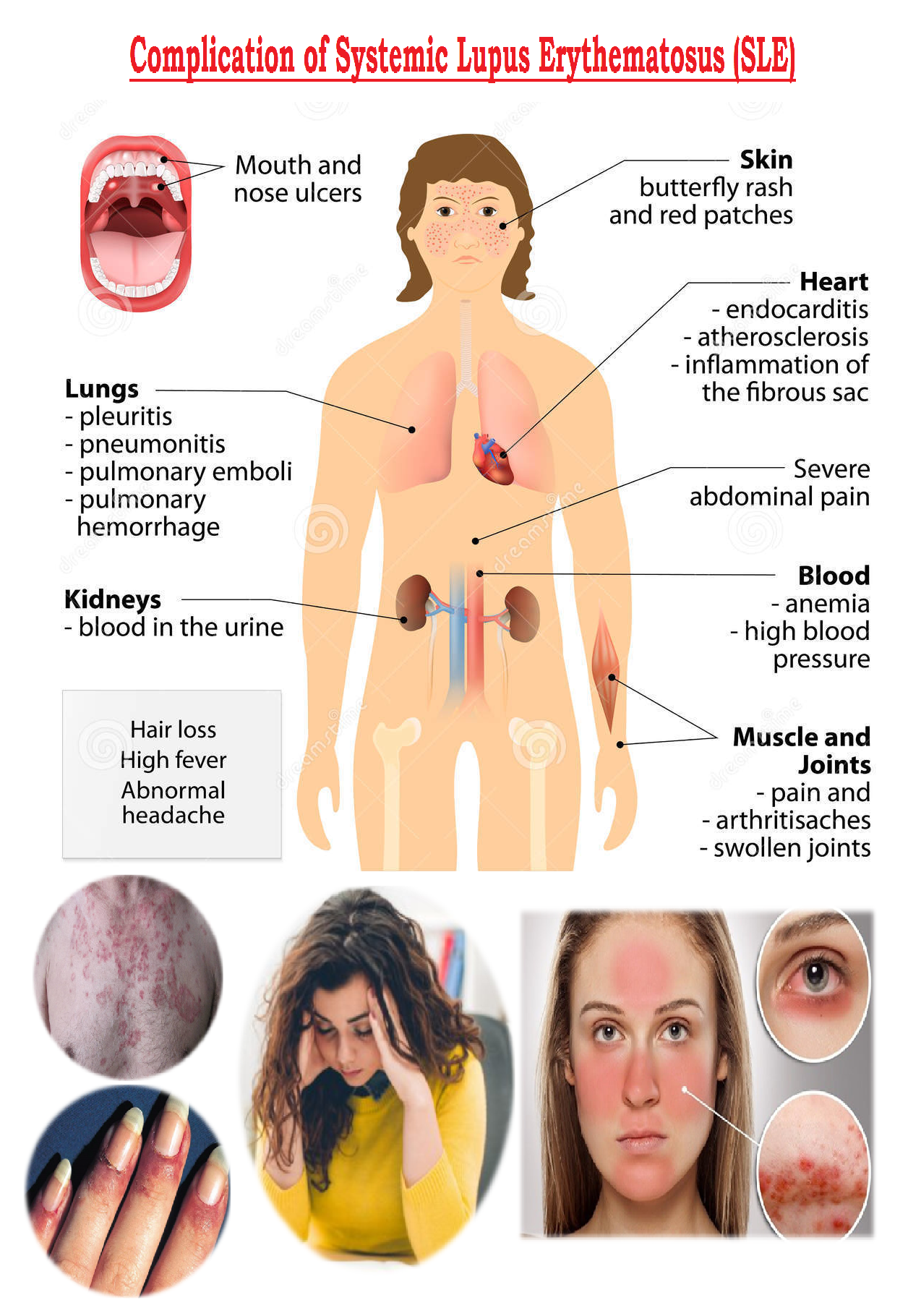
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) MedicoInfo
Systemic lupus erythematosus Abbreviation: SLE A multisystem autoimmune disease that particularly affects women of childbearing age and leads to chronic inflammatory reactions in a variety of organs, including the skin, kidney, and joints. Typical findings include fever and fatigue, a malar rash (facial "butterfly rash"), myalgia, and arthritis.
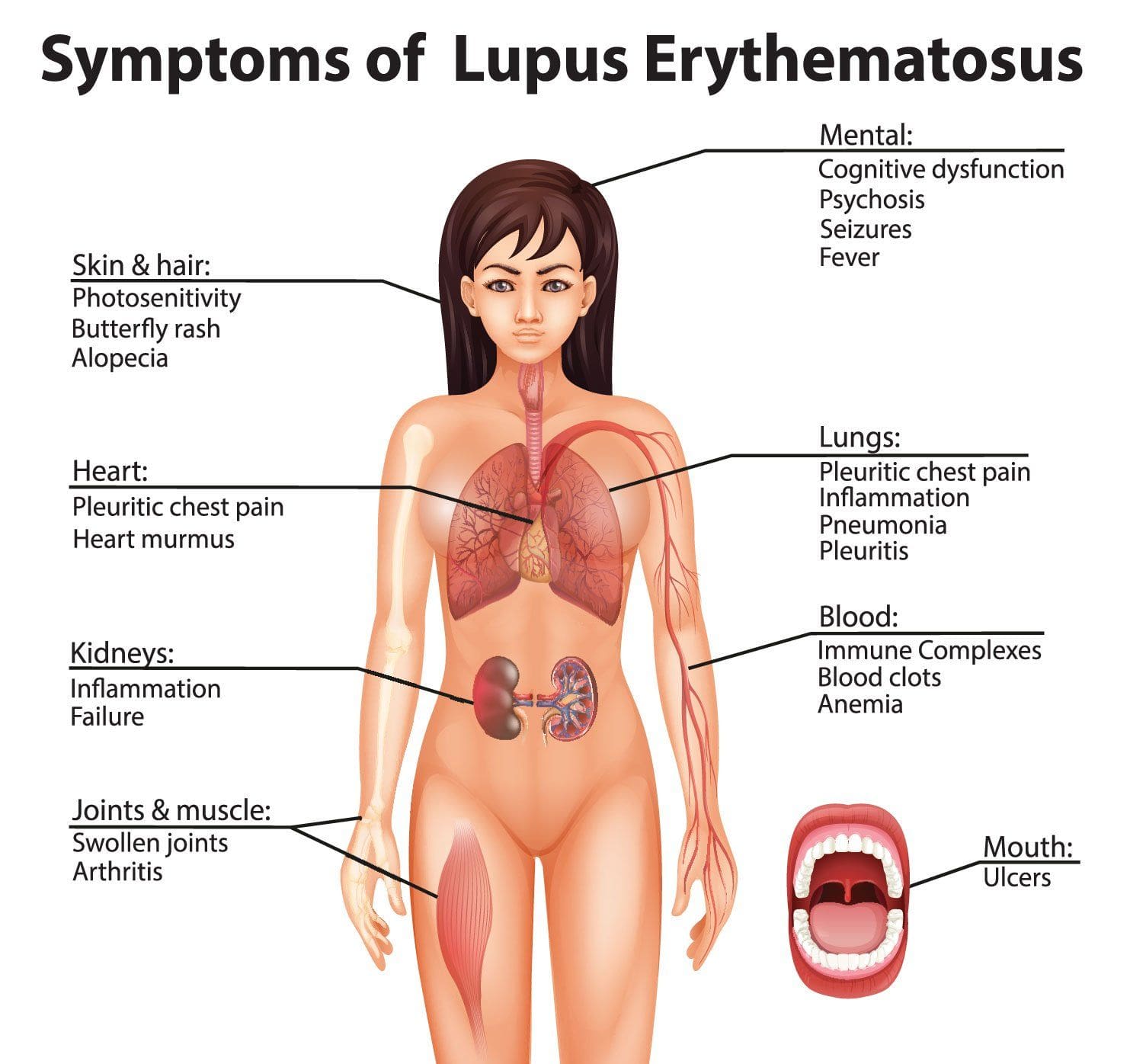
An Overview On Systemic Lupus Erythematosus El Paso, TX Sciatica Pain and Treatment Clinic
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a multisystem autoimmune disease that predominantly affects women of childbearing age and is the most common form of lupus. The exact cause is still unknown, but hormonal and immunological features and genetic predisposition are considered likely etiological factors.

[Figure, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus] StatPearls NCBI Bookshelf
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a multisystem autoimmune disease characterized by the involvement of almost every organ of the body, a broad spectrum of clinical manifestations, and several immune-mediated abnormalities leading to multiple organ dysfunction [ 1 ].
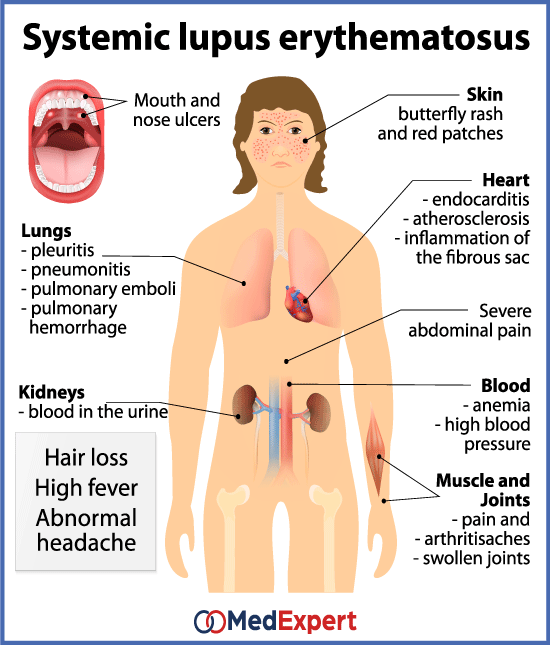
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus MED Expert
Vascular disease is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with systemic autoimmune diseases, particularly systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Although comorbid cardiovascular risk.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Pictures, Symptoms, Causes, Treatment (2018 Updated)
SLE: a challenging disease with a fascinating chronicle. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic systemic autoimmune disease of variable severity and course, characterised by a tendency for flare ().1 In SLE, both innate and adaptive immune responses are involved.Interaction of genes with environmental factors leads to numerous immunologic alterations that culminate into persistent.

EULAR/ACR Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Classification Criteria Update Rheumatology Advisor
Systemic lupus erythematosus has many guises, but the unifying feature is the presence of antibodies against double-stranded DNA in almost all patients. This review provides data that show that suc.

Lupus Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Causes, Sign & Symptoms
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a severe multisystem autoimmune disease that can cause injury in almost every body system. While considered a classic example of autoimmunity, it is still relatively poorly understood. Treatment with immunosuppressive agents is challenging, as many agents are relatively non-specific, and the underlying disease is characterized by unpredictable flares and.
Lupus Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Causes, Sign & Symptoms
Clinical manifestations - Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a heterogeneous autoimmune disease with a wide range of clinical and serologic manifestations that can affect virtually any organ. The disease course is often marked by remissions and relapses and may vary from mild to severe.

Clinical considerations in the diagnosis and management of systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is the most common type of lupus. SLE is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks its own tissues, causing widespread inflammation and tissue damage in the affected organs. It can affect the joints, skin, brain, lungs, kidneys, and blood vessels.